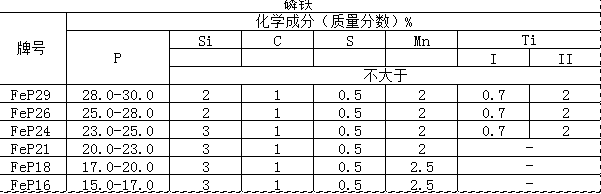
Ferrophosphorus is obtained from the phosphorus-making electric furnace. It is a symbiotic compound containing 20-26% phosphorus and 0.1-6% silicon, which can change the corrosion resistance and chipping of steel. Ferrophosphorus is used as an alloying agent in the steelmaking industry and can also produce phosphate. There are two varieties of ferrophosphorus produced in China, FeP1 and FeP2, which contain 15-20% phosphorus. The atomic number of phosphorus is 15, atomic weight is 30.97, the outer electronic structure is 3S3P, density 1.83g / cm3 (white phosphorus) and 2.2g / cm3 (red phosphorus), melting point 44 ℃, boiling point 257 ℃. Phosphides such as Fe3P, Fe2P, FeP, FeP2 exist. Phosphorus containing 18% to 25% ferrophosphorus has a melting temperature range of 1100 to 1250 ° C and a density of 5.8 to 6.5 g / cm3. Phosphorus is a harmful impurity for most steels. But in some cases it has its special role. For example, the addition of phosphorus to certain steel types can improve the strength, corrosion resistance and workability of the steel, but increases the brittleness of the steel. The addition of phosphorus in the cast iron can improve the fluidity of the molten iron, thereby improving the performance and surface quality of the casting; the gray cast iron contains 0.5% phosphorus, which can increase its tensile strength. The wear-resistant cast iron contains about 0.15% of phosphorus, which can significantly improve its wear resistance.
The train brake shoe contains 0.7% to 1.0% phosphorus, forming a uniform binary phosphorus eutectic structure in the casting and distributed in a network. Phosphorus eutectic has high hardness, which not only improves the degree of wear resistance, but also improves thermal conductivity and heat resistance. Make the wear surface uniform, and it is not easy to produce sparks when rubbing. The ferrophosphorus containing 20% phosphorus is ground into ultrafine powder, which can replace ultrafine zinc powder as coating. Ferrophosphorus is also a protective substance for radioactive radiation.
|

